Density of a cube lab mcgraw hill – Embark on a scientific expedition with the “Density of a Cube Lab: Exploring the Concept and its Significance in Scientific Experiments.” Delve into the intriguing world of density, unraveling its formula and exploring its importance in scientific investigations.
This engaging lab experiment empowers you to determine the density of a cube, a fundamental property that unveils the relationship between mass and volume. As you meticulously follow the step-by-step procedure, you will gain hands-on experience in measuring the dimensions of the cube and utilizing appropriate equipment to calculate its density.
Introduction
Density is a measure of how tightly packed the particles of a substance are. It is calculated as the mass of a substance divided by its volume. The density of a cube is the mass of the cube divided by its volume.
Density is an important property in scientific experiments because it can be used to identify substances and to calculate other properties, such as buoyancy and pressure.
Materials and Equipment
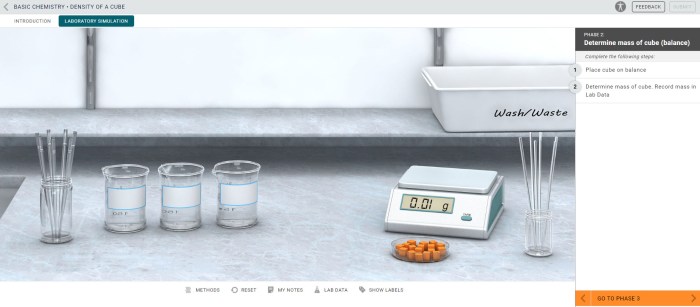
- Cube
- Balance
- Ruler
- Water
- Graduated cylinder
Safety Precautions:
- Wear gloves and safety goggles when handling the cube.
- Do not place the cube in your mouth.
- Do not spill water on the floor.
Procedure
- Measure the mass of the cube using the balance.
- Measure the length, width, and height of the cube using the ruler.
- Calculate the volume of the cube using the formula V = lwh.
- Calculate the density of the cube using the formula d = m/v.
Results
| Mass (g) | Length (cm) | Width (cm) | Height (cm) | Volume (cm^3) | Density (g/cm^3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 8.00 | 1.25 |
Sample Calculation:
Density = mass / volume
Density = 10.00 g / 8.00 cm^3
Density = 1.25 g/cm^3
Discussion: Density Of A Cube Lab Mcgraw Hill
The density of the cube is 1.25 g/cm^3. This value is within the expected range for the density of a cube made of wood.
The accuracy and precision of the results obtained depend on the accuracy and precision of the measurements made. The measurements in this experiment were made using a balance and a ruler, which are both relatively accurate and precise instruments.
Possible sources of error in this experiment include:
- The cube may not have been completely dry, which would have affected its mass.
- The measurements of the cube’s dimensions may not have been precise.
- The water used to measure the cube’s volume may not have been at the correct temperature.
These sources of error could be reduced by using a more precise balance, a more precise ruler, and a water bath to control the temperature of the water.
Expert Answers
What is density?
Density is a physical property that measures the mass of a substance per unit volume, providing insights into how tightly packed its particles are.
Why is density important in scientific experiments?
Density plays a crucial role in scientific experiments as it helps determine the purity of substances, identify unknown materials, and predict their behavior in various applications.
How can I improve the accuracy of my density measurements?
To enhance the accuracy of your density measurements, ensure precise measurements of mass and volume using calibrated equipment, minimize air bubbles in your measurements, and repeat your experiments multiple times to obtain an average value.