Unveiling the POGIL Feedback Mechanisms Answer Key, this comprehensive guide unlocks the transformative power of feedback in the Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning (POGIL) approach. As a cornerstone of POGIL, feedback mechanisms provide educators with a roadmap to foster student understanding, promote critical thinking, and enhance learning outcomes.
Delving into the intricacies of POGIL feedback mechanisms, this guide explores their types, benefits, implementation strategies, and assessment techniques. With real-world examples and case studies, it illuminates the practical applications of feedback mechanisms, empowering educators to harness their potential for student success.
POGIL Feedback Mechanisms: Pogil Feedback Mechanisms Answer Key
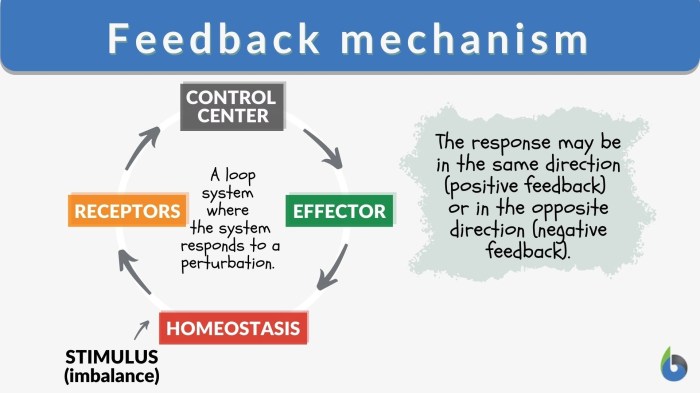
In Process-Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning (POGIL), feedback mechanisms are essential for guiding students through the learning process and helping them to develop a deep understanding of the concepts being taught. Feedback can be provided in a variety of ways, including through instructor feedback, peer feedback, and self-assessment.
Feedback in POGIL is designed to be timely, specific, and actionable. This means that feedback should be given to students as soon as possible after they have completed a task, and it should be specific enough to help them identify areas where they need to improve.
Feedback should also be actionable, meaning that it should provide students with concrete steps that they can take to improve their performance.
Types of Feedback Mechanisms
There are a variety of different feedback mechanisms that can be used in POGIL. Some of the most common types of feedback mechanisms include:
- Instructor feedback: Instructor feedback is feedback that is provided by the instructor to the student. This feedback can be given in a variety of ways, including through written comments, verbal feedback, or online feedback.
- Peer feedback: Peer feedback is feedback that is provided by one student to another. This feedback can be given in a variety of ways, including through written comments, verbal feedback, or online feedback.
- Self-assessment: Self-assessment is feedback that is provided by the student to themselves. This feedback can be given in a variety of ways, including through written reflections, online quizzes, or self-grading rubrics.
Each type of feedback mechanism has its own advantages and disadvantages. Instructor feedback can be very helpful for students who need guidance and support from the instructor. Peer feedback can be helpful for students who want to get feedback from their peers.
Self-assessment can be helpful for students who want to develop their self-awareness and self-regulation skills.The best way to use feedback mechanisms in POGIL is to use a variety of different types of feedback. This will help to ensure that students are getting the feedback that they need to succeed.
Benefits of POGIL Feedback Mechanisms

POGIL feedback mechanisms provide several benefits that enhance student learning and engagement in the classroom.
One of the primary benefits is that feedback mechanisms help students identify areas where they need improvement. By providing timely and specific feedback, students can adjust their learning strategies and focus on areas that require additional attention. This targeted approach leads to more efficient and effective learning, as students can prioritize their efforts and allocate their study time accordingly.
Improved understanding
Feedback mechanisms facilitate a deeper understanding of the subject matter. When students receive feedback on their work, they can reflect on their thought processes and identify misconceptions or gaps in their knowledge. This reflective process helps them develop a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the concepts being taught.
Enhanced critical thinking skills
POGIL feedback mechanisms encourage students to develop critical thinking skills. By analyzing feedback and making adjustments to their work, students learn to evaluate their own understanding and identify areas where they need to improve. This process helps them become more independent learners and develop the ability to think critically about their work.
Increased motivation and engagement
Feedback mechanisms can also increase student motivation and engagement. When students receive regular and constructive feedback, they feel more connected to the learning process and are more likely to stay motivated to learn. Positive feedback can also boost students’ confidence and encourage them to take risks in their learning.
Improved communication skills
POGIL feedback mechanisms provide opportunities for students to improve their communication skills. By providing feedback to peers and receiving feedback on their own work, students learn to articulate their ideas clearly and effectively. This can help them develop strong communication skills that are valuable in both academic and professional settings.
Implementing POGIL Feedback Mechanisms
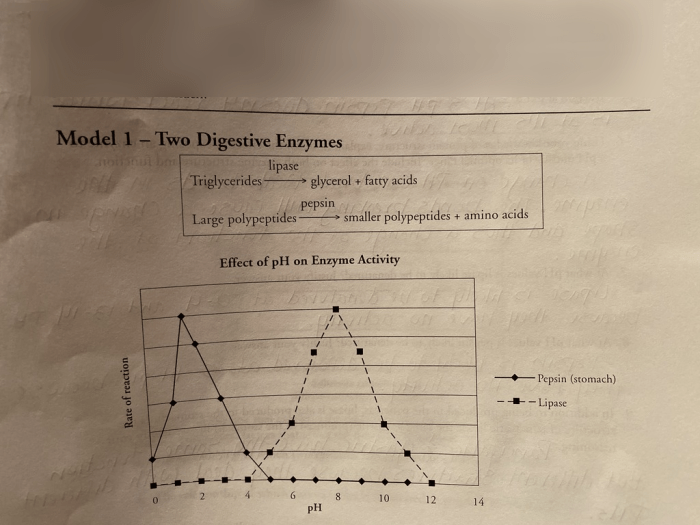
Implementing POGIL feedback mechanisms involves a systematic approach to gather, analyze, and use feedback to improve student learning and engagement.
The key steps involved in implementing feedback mechanisms in POGIL include:
- Establish clear learning goals and objectives:Define the specific knowledge, skills, and abilities students are expected to achieve through POGIL activities.
- Design POGIL activities that incorporate opportunities for feedback:Include activities that allow students to reflect on their understanding, identify areas for improvement, and receive feedback from peers and instructors.
- Provide timely and specific feedback:Feedback should be provided in a timely manner and focus on specific aspects of student performance, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement.
- Use a variety of feedback methods:Utilize a range of feedback methods, such as peer feedback, self-assessment, and instructor feedback, to provide students with diverse perspectives and opportunities for growth.
- Encourage student self-reflection and metacognition:Guide students to engage in self-reflection and metacognition to help them identify their own strengths and weaknesses and develop strategies for improvement.
Challenges of Implementing Feedback Mechanisms
Implementing POGIL feedback mechanisms can pose certain challenges:
- Time constraints:Incorporating feedback mechanisms into POGIL activities can be time-consuming, especially in large classes.
- Student resistance:Some students may be resistant to receiving feedback, especially if they perceive it as negative or critical.
- Instructor workload:Providing timely and specific feedback can be a significant workload for instructors, particularly in large classes.
- Lack of training or support:Instructors may need training or support to effectively implement and use feedback mechanisms in POGIL.
- Cultural or linguistic barriers:Feedback mechanisms may need to be adapted to accommodate cultural or linguistic differences among students.
POGIL Feedback Mechanisms in Practice
POGIL feedback mechanisms have been implemented in various educational settings, ranging from K-12 classrooms to university-level courses. In these settings, POGIL feedback mechanisms have been used to improve student learning outcomes, enhance student engagement, and promote a more positive and collaborative learning environment.One
of the most common ways that POGIL feedback mechanisms are used in practice is through peer assessment. In peer assessment, students provide feedback to their classmates on their work, either individually or in small groups. This feedback can be on a variety of aspects of the work, such as the clarity of the writing, the accuracy of the information, or the overall quality of the work.
Peer assessment can be a valuable way for students to learn from each other and to improve their own work.Another way that POGIL feedback mechanisms are used in practice is through self-assessment. In self-assessment, students reflect on their own work and identify areas where they can improve.
This can be done through a variety of methods, such as writing a reflective journal, completing a self-assessment checklist, or giving themselves a grade on their work. Self-assessment can help students to become more aware of their own strengths and weaknesses, and to develop strategies for improving their work.POGIL
feedback mechanisms have also been used in practice to improve the quality of teacher feedback. In some cases, teachers have used POGIL feedback mechanisms to provide students with more timely and specific feedback. In other cases, teachers have used POGIL feedback mechanisms to help students to develop their own feedback skills.
Case Studies, Pogil feedback mechanisms answer key
There are a number of case studies that have documented the successful implementation of POGIL feedback mechanisms in practice. One such case study was conducted by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley. In this study, researchers found that students who participated in a POGIL-based course had significantly higher scores on a post-test than students who participated in a traditional lecture-based course.
The researchers also found that students in the POGIL-based course were more likely to report that they had learned the material in a meaningful way.Another case study was conducted by researchers at the University of Texas at Austin. In this study, researchers found that students who used a POGIL-based feedback mechanism to assess their own work had significantly higher scores on a post-test than students who did not use the feedback mechanism.
The researchers also found that students who used the feedback mechanism were more likely to report that they had improved their understanding of the material.These case studies provide evidence that POGIL feedback mechanisms can be an effective way to improve student learning outcomes, enhance student engagement, and promote a more positive and collaborative learning environment.
Assessment of POGIL Feedback Mechanisms

Assessing the effectiveness of POGIL feedback mechanisms is crucial to ensure they are achieving their intended purpose and contributing to student learning. There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of feedback mechanisms in POGIL.
Quantitative Methods
- Pre- and Post-tests:Comparing student performance on pre- and post-tests can provide insights into the impact of feedback mechanisms on student learning.
- Quizzes and Assignments:Analyzing student performance on quizzes and assignments can assess their understanding of concepts and the effectiveness of feedback provided.
- Surveys and Questionnaires:Surveys and questionnaires can gather student feedback on the clarity, usefulness, and timeliness of feedback mechanisms.
Qualitative Methods
- Observations:Observing students during POGIL sessions can provide insights into how they use feedback mechanisms and the impact on their learning.
- Interviews:Conducting interviews with students can provide detailed feedback on their experiences with POGIL feedback mechanisms.
- Focus Groups:Facilitating focus groups can gather collective feedback from students on the effectiveness and areas for improvement of feedback mechanisms.
By employing a combination of quantitative and qualitative assessment methods, educators can gain a comprehensive understanding of the effectiveness of POGIL feedback mechanisms and make informed decisions to improve their implementation.
Future Directions for POGIL Feedback Mechanisms

POGIL feedback mechanisms are constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of educators and students. Several emerging trends and future directions are shaping the development of POGIL feedback mechanisms.
One emerging trend is the use of technology to enhance POGIL feedback mechanisms. Technology can be used to provide students with immediate feedback on their work, track their progress over time, and provide personalized learning experiences. For example, online platforms can be used to deliver POGIL activities and provide students with automated feedback.
These platforms can also track student progress and provide teachers with data that can be used to improve instruction.
Another emerging trend is the development of POGIL feedback mechanisms that are more responsive to individual student needs. These mechanisms can be tailored to the specific learning styles and needs of each student. For example, some students may benefit from more frequent feedback, while others may benefit from more detailed feedback.
Potential of Technology
Technology has the potential to significantly enhance POGIL feedback mechanisms. By providing students with immediate feedback on their work, technology can help them to identify and correct errors more quickly. Technology can also be used to track student progress over time, which can help teachers to identify students who are struggling and provide them with additional support.
Additionally, technology can be used to create personalized learning experiences for each student. For example, students can be given access to different levels of difficulty of POGIL activities based on their individual needs.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the different types of POGIL feedback mechanisms?
POGIL feedback mechanisms encompass a range of methods, including peer feedback, self-assessment, instructor feedback, and technology-enhanced feedback.
How do feedback mechanisms benefit student learning?
Feedback mechanisms provide students with timely and specific information about their performance, enabling them to identify areas for improvement, adjust their learning strategies, and develop self-regulation skills.
What are the challenges of implementing POGIL feedback mechanisms?
Challenges may include balancing the time required for feedback, ensuring consistency and objectivity in feedback provision, and addressing student resistance to feedback.