Lenders in the loanable funds market consist of a diverse group of financial institutions that play a crucial role in facilitating the flow of funds between savers and borrowers. These institutions, which include banks, credit unions, and insurance companies, serve as intermediaries in the financial system, channeling excess savings into productive investments.
The decisions made by lenders in the loanable funds market have a significant impact on the availability of credit, interest rates, and overall economic growth. By understanding the characteristics, motivations, and challenges faced by lenders, we can gain valuable insights into the functioning of the financial system and its implications for economic policy.
Lenders in the Loanable Funds Market
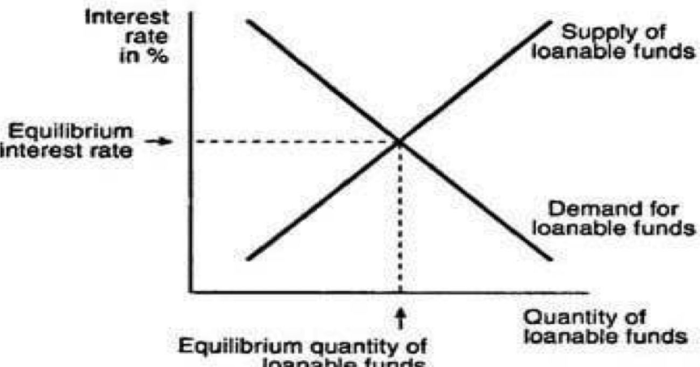
Lenders in the loanable funds market play a crucial role in the financial system by providing capital to borrowers. They act as intermediaries between those with excess funds (savers) and those in need of funds (borrowers). Lenders include banks, credit unions, insurance companies, pension funds, and government agencies.
Factors Influencing Lenders’ Decisions to Lend, Lenders in the loanable funds market consist of
Several factors influence lenders’ decisions to lend, including:
- Creditworthiness of the Borrower:Lenders assess the borrower’s ability to repay the loan based on their credit history, income, and assets.
- Loan Amount and Term:The size and duration of the loan affect the lender’s risk and return.
- Interest Rates:Lenders consider the prevailing interest rates and the potential return on their investment.
- Economic Conditions:Economic conditions, such as inflation and unemployment, can impact lenders’ willingness to lend.
- Government Regulations:Government regulations, such as capital requirements and consumer protection laws, can influence lender behavior.
Characteristics of Lenders: Lenders In The Loanable Funds Market Consist Of
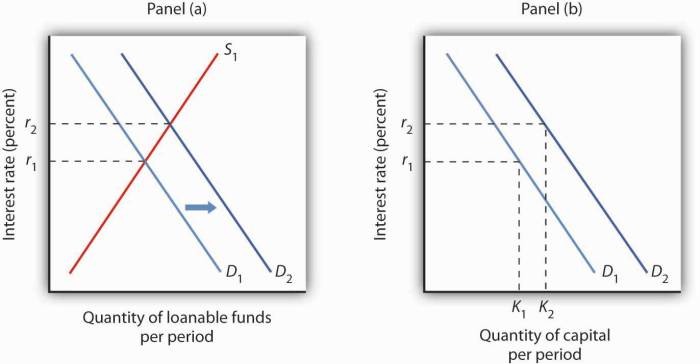
Key characteristics of lenders in the loanable funds market include:
Risk Aversion
Lenders are generally risk-averse, meaning they prefer loans with lower default risk. This characteristic affects the availability of loanable funds, as lenders may be hesitant to lend to borrowers with higher credit risk.
Liquidity
Lenders need to maintain a certain level of liquidity to meet the demands of depositors and other creditors. This liquidity constraint can limit the amount of loanable funds available.
Government Regulations
Government regulations, such as capital requirements and reserve ratios, can impact lenders’ characteristics. These regulations aim to ensure the stability of the financial system and protect depositors.
Lenders’ Impact on Interest Rates
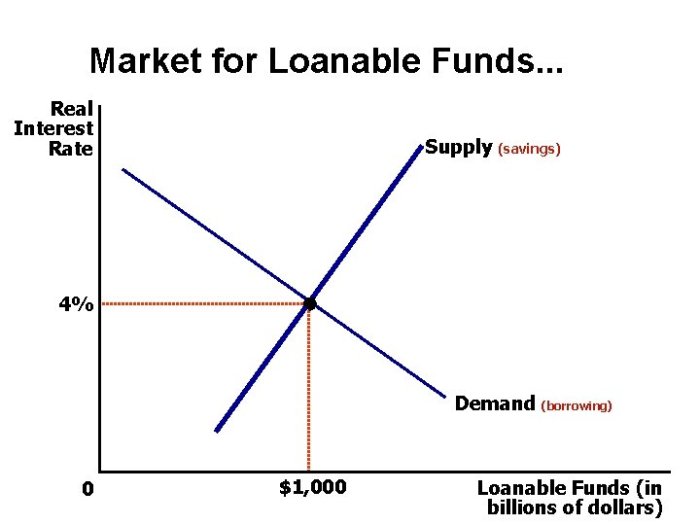
Lenders’ decisions influence interest rates in the loanable funds market through the following mechanisms:
Supply and Demand
Lenders’ willingness to lend affects the supply of loanable funds. An increase in the supply of loanable funds leads to lower interest rates, while a decrease leads to higher interest rates.
Risk Premiums
Lenders charge risk premiums on loans to compensate for the risk of default. Higher risk premiums lead to higher interest rates for borrowers with lower creditworthiness.
Expectations
Lenders’ expectations about future economic conditions and inflation can also impact interest rates.
Lenders’ Role in Economic Growth
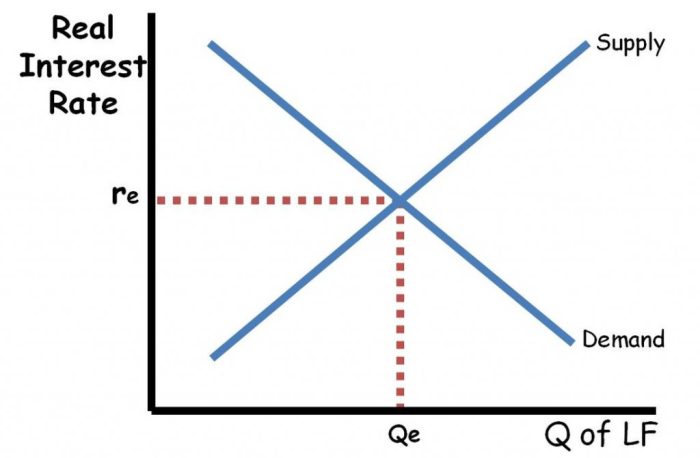
Lenders play a vital role in promoting economic growth by:
Providing Capital for Businesses
Businesses rely on loans to finance their operations, invest in new equipment, and expand their businesses. Lenders provide the capital that businesses need to grow and create jobs.
Providing Capital for Consumers
Consumers also rely on loans to purchase homes, cars, and other goods and services. Lenders provide the capital that consumers need to make these purchases, which stimulates economic activity.
Risk Aversion and Economic Growth
Lenders’ risk aversion can have a positive or negative impact on economic growth. On the one hand, it can help to ensure the stability of the financial system. On the other hand, it can limit the availability of loanable funds and hinder economic growth.
Clarifying Questions
What are the different types of lenders in the loanable funds market?
Lenders in the loanable funds market include banks, credit unions, insurance companies, pension funds, and government agencies.
How do lenders decide whether to lend?
Lenders consider factors such as the creditworthiness of the borrower, the purpose of the loan, the amount of collateral offered, and the prevailing interest rates.
What impact do lenders have on interest rates?
Lenders’ decisions regarding the supply of loanable funds influence interest rates, with higher supply leading to lower rates and vice versa.