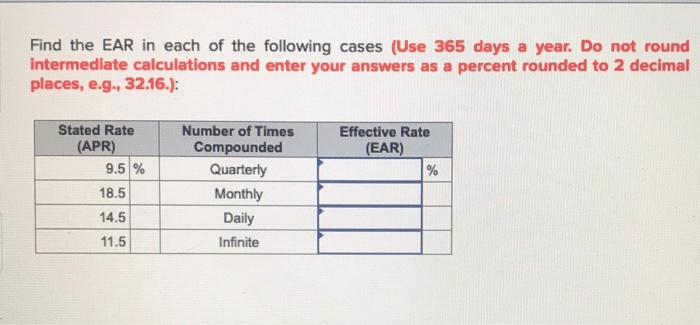
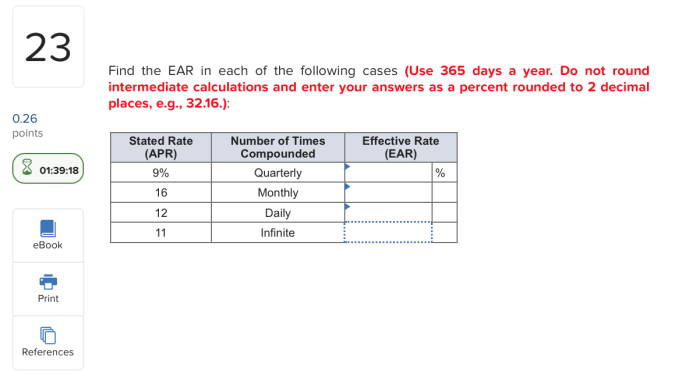
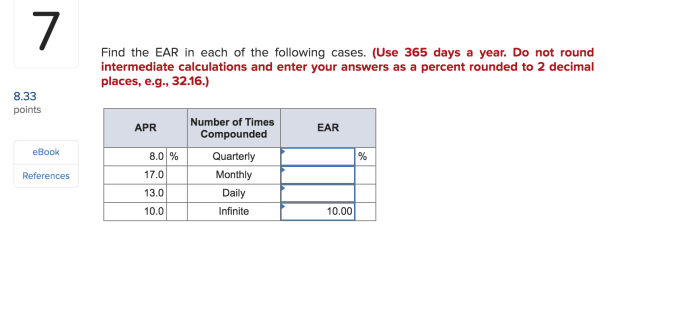
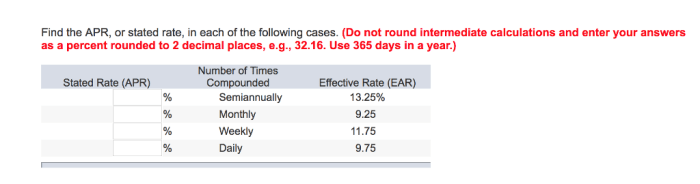
Find the ear in each of the following cases: – Embarking on a journey to explore the fascinating world of ears, this discourse delves into the diverse locations where ears can be found, their medical significance, cultural implications, artistic representations, and intricate anatomy and function. Prepare to be captivated as we uncover the hidden depths of this remarkable sensory organ.
From the intricate workings of the inner ear to the cultural significance of ear adornments, this exploration unravels the multifaceted nature of ears, shedding light on their profound impact on our physical, social, and artistic landscapes.
1. Identify Ear Locations
Ears, essential sensory organs, are found in various locations on the human body, each serving a specific purpose:
- Head:The primary location of ears, where they are positioned laterally on either side of the head. These ears, known as the external ears or auricles, are responsible for sound collection and direction.
- Thoracic Cavity:The thoracic cavity, also known as the chest, contains the inner ears. Embedded deep within the temporal bones, these ears are responsible for balance and hearing.
- Abdomen:The abdomen, or belly, also houses inner ears. Located near the kidneys, these ears contribute to the regulation of blood pressure and fluid balance.
The variations in ear structures across different body parts reflect their specific functions. The external ears, with their complex shapes and folds, are designed to capture and funnel sound waves towards the inner ears. In contrast, the inner ears, housed within the skull, are delicate structures responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals and maintaining balance.
2. Medical Contexts for Ear Identification
Ear identification plays a crucial role in medical diagnosis and treatment. Various medical procedures involve identifying ears:
- Otoscopy:A non-invasive procedure that involves using an otoscope to examine the external ear canal and eardrum. It aids in diagnosing ear infections, perforations, and other conditions.
- Audiometry:A series of tests that assess hearing thresholds and abilities. It helps identify hearing loss, tinnitus, and other ear-related disorders.
- Tympanometry:A test that measures the movement of the eardrum in response to sound waves. It aids in diagnosing middle ear infections and other conditions affecting the eardrum.
Ear identification is also crucial in medical emergencies. For example, in cases of trauma or unconsciousness, identifying ears can help determine the patient’s orientation and potential injuries.
3. Cultural and Social Significance of Ears: Find The Ear In Each Of The Following Cases:
Ears hold cultural and social significance beyond their sensory functions:
- Ear Piercings and Adornments:In many cultures, ear piercings and adornments, such as earrings, have been practiced for centuries. They symbolize cultural identity, beauty, and social status.
- Ear Modifications:In some cultures, ear modifications, such as ear stretching or gauging, are practiced as a form of body art or cultural expression.
- Nonverbal Communication:Ears play a role in nonverbal communication. For example, covering ears can indicate a desire to block out noise, while pulling on ears can convey discomfort or nervousness.
The cultural and social significance of ears varies widely across societies, reflecting the diverse beliefs and practices of different cultures.
4. Artistic Depictions of Ears
Ears have been a subject of artistic depictions throughout history:
- Paintings:Ears have been portrayed in paintings to convey emotions and character traits. For example, Vincent van Gogh’s self-portraits often featured exaggerated ears, symbolizing his emotional state.
- Sculptures:In sculptures, ears have been used to depict realism and convey the subject’s personality. The iconic “David” sculpture by Michelangelo features detailed ears, contributing to the overall anatomical accuracy of the work.
- Other Artistic Mediums:Ears have also been incorporated into other artistic mediums, such as photography, literature, and music, often serving as metaphors or symbols.
The artistic depiction of ears has evolved over time, reflecting changing cultural and aesthetic sensibilities.
5. Ear Anatomy and Function
The ear, a complex organ, consists of three main sections:
- External Ear:The visible portion of the ear, consisting of the auricle and ear canal. It collects and directs sound waves towards the middle ear.
- Middle Ear:A small, air-filled cavity located behind the eardrum. It contains the ossicles (tiny bones) that transmit sound vibrations to the inner ear.
- Inner Ear:The innermost part of the ear, embedded within the temporal bone. It contains the cochlea (involved in hearing) and the vestibular system (responsible for balance).
Each part of the ear plays a specific role in hearing, balance, and other sensory processes.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the primary function of the ear?
The ear’s primary function is to facilitate hearing and balance, enabling us to perceive sound and maintain spatial orientation.
How do cultural practices influence ear modifications?
Cultural practices can significantly influence ear modifications, such as ear piercings, stretching, and adornments, which often hold deep symbolic or aesthetic meanings within specific communities.
What medical procedures involve ear identification?
Ear identification is crucial in medical procedures such as otoscopy, audiometry, and surgical interventions, allowing healthcare professionals to assess ear health and diagnose potential issues.